摘要:海南大学农学院,海南省热带生物资源可持续利用重点实验室汤华教授与相关课题组成员研究了香蕉叶片枯萎病与基因的差异表达的关系,相关成果已在线发表于《Molecular Plant Breeding》。
香蕉枯萎病是一种由香蕉枯萎病引起的破坏性真菌疾病,并严重影响香蕉的规模生产与栽培。为了研究香蕉枯萎病病的发病机理,通过cDNA-AFLP技术确定诱导或抑制病菌引起的微小的达转录差异。最终通过sqRT-PCR筛选出6个重要基因来分析其表达模式,并确认了其与香蕉枯萎病的发病机理的相关性。
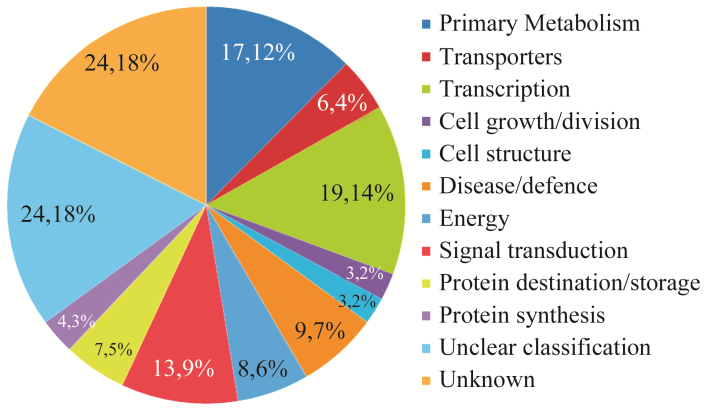
ESTs功能目录的cDNA-AFLP分布
原文链接:Differential expressed genes of banana leaves induced by Fusarium wilt disease
Fusarium wilt of banana is a destructive fungus disease caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cubense. This disease had harmful effects on banana planting and its industrial production. In order to study the pathogenic mechanism of banana Fusarium wilt disease, we used cDNA-AFLP technique to identify differential expressed transcripts that were induced or inhibited by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cubense tropical race 4 infection. Among 223 isolated cDNA fragments, we sequenced and get 137 unique banana cDNAs that involved in different functions, including disease and defense response, transcription regulation, signal transduction, primary metabolism, energy metabolism, cell growth and division, protein destination and storage, and so on. Among these genes, 8 ESTs were related to disease and defense response including NBS-LRR type resistance gene, hot shock protein, and alcohol dehydrogenase; 19 ESTs were related to transcriptional regulation including transcription factor MYB and MYC, zinc finger protein, and Glycine-rich RNA binding protein; 12 ESTs were related to signal transduction including the Ras-related nuclear proteins. We choose out 6 important genes to analyze the expression patterns by sqRT-PCR, and confirm their relationship with pathogenic mechanism of banana Fusarium wilt.
日期:2015-11-08 新闻作者:Candy 来源:Molecular Plant Breeding
链接:http://biopublisher.ca/index.php/mpb/article/view/2050

